Modern Pros and Cons of Biogas

Natural gas is a limited resource on our planet, but biogas can be produced from any form of organic waste.
This means that until we have people, animals and plants on the planet, the organic waste produced daily can be turned into biogas, which is cleaner than natural gas.
Biogas is considered cleaner than the natural gas provided by your utility company, because by capturing methane emissions from decaying organic waste (which otherwise would be released in the atmosphere), biogas helps reducing the greenhouse effect on the planet.
What is Biogas? – Definition
Biogas is a green gas produced from organic waste, and is a cleaner fuel because is free of volatile impurities being produced through an organic matter degradation process.
We can consider biogas a sustainable fuel due to the fact that the organic degradation process used to produce this gas allows an economic development of the area. Waste is turned into energy, so the consumption of fossil fuels is reduced. This way, the local economy becomes self-sustainable by turning waste into useful products.
Biogas is also an eco-friendly fuel because its combustion does not intensify the greenhouse effect on the planet.
This green fuel can be used for cooking, residential heating, electricity generation and as a cleaner fuel for vehicles with modified engines.
More than that, if we purify the raw biogas produced in digesters, we can inject it into the natural gas network to be used by consumers as a clean fuel (neutral fuel).
How Does a Complex Biogas Plant Work?
The main source of air pollution in the cities, is the large number of conventional vehicles on the streets.
A complex biogas plant does not produce only biogas in gaseous form and fertilizers, because it can produce liquefied biogas as well.
The plant receives every day a good amount of organic waste and residues from local farms and food production facilities.
A biogas plant producing biogas in gaseous but also in liquefied form, will use two plants instead of one: a production plant and a liquefaction plant.
The raw organic materials called ‘substrates’ arrive at the plant transported in tanks.
The Production Plant
Before being fed into the digestion chamber, the organic waste is macerated and mixed. The mixture is warmed at a temperature of around 100°F (38°C), and after that is pumped into the digestion chamber without impurities.
The fermentation process takes place in a hermetically sealed chamber (anaerobic digestion), where bacteria break down enzymes and other components present in the mixture of organic waste, to release biogas.
The digestion chamber receives new organic material every day and this ensures a continuous production of biogas and biofertilizers.
According to this study, the biogas produced in the digestion chamber contains between 50 to 70% methane, between 30 to 40% carbon dioxide, small amounts of water vapor, hydrogen sulphide, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and traces of ammonia and siloxanes.
The biofertilizers produced are pumped into a storage tank and used later in agriculture.
A biogas plant provides the local plant growers with a permanent supply of biofertilizers, which supports an organic and sustainable agriculture.
An upgrading plant is used to refine the raw biogas produced in the digester chamber. The refined biogas reaches a methane concentration of 97%.
The Liquefaction Plant
The refined biogas is now sent to the liquefaction plant where a large volume of it is turned into liquefied biogas by lowering the temperature of the gas to – 261°F (-163°C).
Liquefied biogas can be transported and stored like conventional fuels obtained from petroleum.
By modifying the diesel engine used by trucks and buses, liquified biogas can be used as a sustainable fuel that releases a reduced amount of emissions.
Liquefied biogas works well in gasoline engines, but to be used in diesel engines we have to mix biogas with diesel.
In the EU, beside biogas plants we can also find biomethane plants, which are very developed in countries like Gemrany, France and the UK.
Pros of Biogas
Biogas is a biofuel produced from organic waste, which means that it provides more benefits than drawbacks.
1. Is a Renewable Resource
Biogas is maybe the most underestimated natural and never-ending resource available on the planet.
Waste incineration in landfills represents only a waste of resources that otherwise would be turned into biogas through anaerobic digestion (the organic waste), and useful materials for the industry (the solid part of the waste consisting of recyclable materials).
A circular economy must copy nature’s cycle in order to turn waste materials into green fuels, clean energy and other useful products such as fertilizers and compost.
Biogas is a renewable resource because it can be produced from organic residues (plant and food waste), human waste (from municipal collection), and animal waste (from farms, animal husbandry and breeding).
All these organic materials required for the production of biogas, are produced daily on the planet, which means that until we have plants, people and animals on planet Earth, organic waste will be produced every day and will represent a natural and renewable resource for biogas production.
2. Can Reduce Air Pollution and the Greenhouse Effect on the Planet
Biogas is emission neutral and can reduce the methane emissions in landfills (methane is a greenhouse gas 25 times more potent than CO2).
Air pollution produced by the industry, the energy and the transportation sectors, is the main reason for the increased greenhouse gas effect on the planet, which has already changed the weather conditions.
This shows that climate change is real, and if don’t reduce our impact on the environment, we will suffer greatly.
Organic waste produced by plants, people and animals, that is no longer deposited in landfills, is turned into biogas (a green fuel), fertilizers and compost (useful for soil and plants).
This way, instead of increasing the greenhouse effect on the planet, the methane resulted during the fermentation process is used as fuel, and the other byproducts such as fertilizers and compost are used to create fertile soils.
Liquefied biogas burns cleaner than diesel and can be used in vehicles with combustion engines to reduce emissions.
3. Is a Flexible Fuel
Biogas is considered a flexible fuel due to the fact that can be used as a local or regional energy supply and also as clean fuel for vehicles.
To be used as fuel for vehicles, a part of the biogas produced at the plant is converted into liquefied biogas by lowering the temperature of the gas.
Used as green fuel for vehicles, it generates enough power to move the vehicle and a reduced amount of emissions compared to the conventional fuels based on petroleum (gasoline and diesel).
4. Is A Transportable and Storable Fuel
Biogas can be easily transported and stored regardless of the season or weather conditions.
Turned into liquefied biogas, it can be transported in tanks for liquid fuels. Left in gaseous form, the same amount of biogas would require a tank that is three times larger than the tank used to transport liquefied biogas.
In liquid form, biogas creates the opportunity for more efficient distribution and simpler storage.
5. Biogas Production Has a Positive Impact on the Environment
Consuming municipal, industrial and agricultural waste for the production of biogas has a positive impact on the environment because the natural resource that are limited such as fossil fuels are no longer used for energy, heat and fuel production, or at least the usage of fossil fuels is reduced.
Solid and liquid residues fed to the digester will no longer decompose in nature or landfills, and this will decrease the volume of greenhouse gas emissions released into the atmosphere.
6. Biogas Production Generates Other Useful Products
The digestion chamber used for the production of biogas also produces fertilizers and compost.
All these natural products are used as soil conditioners and fertilizers in agriculture, which improves the crop production.
Compost and fertilizers produced by a biogas plant are very useful for plant growers and farmers.
Cons of Biogas
Unfortunately, there are few drawbacks affecting this renewable resource called biogas.
1. The Technology used to Produce Biogas is not very Efficient
The production of biogas requires large chambers for anaerobic fermentation of the organic waste, and the technology used by biogas plants is quite old and not very efficient.
To improve the technology, the biogas sector requires governmental investments, but sadly, the authorities don’t seem to be interested to invest in the sector, at least not yet.
2.The Biogas Sector is Less Developed
Building a new biogas plant is quite expensive, and this is one of the reasons why biogas has become an important source of clean power for the local economy only in a few countries on the planet.
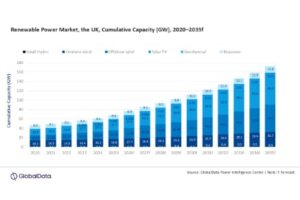
While biogas starts only now to become a more popular source of clean energy and fuels in the United States, in the EU, Germany is a leader in technology and biogas production.

Biogas plant at Apsley Farms in the UK.
The UK already injected biogas in its gas grid for the first time in 2010, and now biogas has become an important source of energy in several cities.
3. Biogas Production Has Some Limitations
Biogas production is more suitable for rural and suburban areas because only there the plant can receive raw organic materials daily such as food waste, manure and plant waste.
A big city can provide mainly food waste, but no manure or plant waste.
The water and the organic material provided by the sewage system of the city will go to a treatment plant, instead of being sent to a biogas plant built near the big city. However, the biogas plant fed by a big city will receive daily only food waste, but no manure or plant waste (that would be available only in the spring and the fall).
4. Biogas Plants Are Affected By Weather And Require Constant Supply of Organic Materials
Inside the fermentation chamber, organic waste is digested at a temperature around 100°F (38°C). In colder climates, the biogas plant will consume additional energy to keep the fermentation chamber at the required temperature.
Biogas plants are very dependent on feedstock supply, so there is no reason to build them in areas where organic waste is not available 24/7.
Conclusion
We all know that natural gas is cleaner than coal and oil, and this low-carbon fossil fuel can successfully replace these dirty sources of energy to lower the emissions.
However, biogas is even cleaner than natural gas, so at least locally, biogas plants could lower the carbon-footprint of each city.